제목 붙이기가 좀 어렵네요
CI로 CMS를 개발하다보니 CI코어와 플러그인, 위젯, 레이아웃 등을 분리해야할 필요성이 생겼습니다.
그리고 플러그인의 특성상 자기 자신만으로도 웹에서 보일 수 있어야 해서 주소체계를 CI의 주소체계로 동일하게 사용해야 했습니다.(변수 전달도 포함)
plugins/
widgets/
layouts/
system/
http://localhost/plugins/control/board/main <- 이렇게 주소를 쓰는데 플러그인중 게시판(board)의 main.tpl.php(템플릿) 파일을 불러옵니다.
위 주소는 application/controllers/plugins.php 에 연결되어있고 그 내용은 다음과 같습니다.
$this->load->model(PLUGPATH.’/’.$this->uri->segment(3).’/Functions’);
// $this->uri->segment(3)=> board 플러그인의 Functions.php 모델을 불러옵니다.
// 플러그인 규칙으로 모델은 Functions.php로 정합니다.
$data=$this->Functions->default_control(); // Functions 모델의 default_control 함수를 호출하는데 그 안에 컨트롤 파일이 들어있습니다.
$this->load->parser(PLUGPATH.’/’.$this->uri->segment(3).’/default/’.$this->uri->segment(4).’tpl.php’, $data);
}
plugins/board/Functions.php
게시판 리스트 가져오는 함수
return $query->result_array(); // result_array()-> CI의 DB함수
}
function default_control (){
$ll = $this->blist(‘test’); //게시판 리스트를 배열로 가져옵니다.
return $ll;
}
└– default_control 부분이 핵심입니다. 컨트롤러에 있어야할 내용이 모델안에 함수로 정의되어 있습니다.
그리고 plusins라는 컨트롤에서 default_control 함수가 처리한 내용을 받아서
CI 템플릿 형태의 파일인 main.tpl.php로 보내줍니다.
위와 같은 작업을 함으로써 application 디렉토리 이외의 외부 디렉토리에서도 MVC 패턴(엄밀히 말하면 아니지만, 모델안에 컨트롤러가 구현되어 있으므로)을
그대로 구현할 수 있습니다. 특히나 다른 개발자가 만든 플러그인 같은 경우 정해진 규약대로만 만들면(Functions.php main.tpl.php 등)
CI의 주소체계를 이용하고 CI 내장함수도 그대로 이용을 할 수가 있습니다.
평상시 개발에서는 구현할 필요가 없지만 외부 개발자들이 만든 플러그인을 사용하는 구조라면 필요합니다.
이 내용을 올리는 가장 큰 목적은 CI의 유연성을 말하고 싶어서 입니다.
이번에 CI로 CMS 작업을 하면서 느낀 것은 CI의 확장성, 유연성입니다. 어느 정도 프레임워크로서의 틀을 가지고 있지만 그 틀을 넘나들 수 있는 유연성을 가지고 있다는 것.
다시 말해 개발자들이 어떻게 구현하느냐에 따라 정말 어떤 구조던지 가능하다는 것입니다.
프레임워크의 편리함(내장함수들의 편리함, 구조화, mvc패턴 등등)을 사용하면서 동시에 개발자의 재량에 따라 얼마든지 기존 구조이외에 것을 이용할 수 있다는 점이 큰 장점이라고 할 수 있겠습니다.
php
PHP Framework CODEIGNITER의 장점과 사용하면서 불편했던 점
먼저 좋은 점은 가볍다 입니다. 확장도 용이하구요.
사용자들이 올려놓은 wiki의 파일이나 플러그인이 이용할만한게 많습니다.
다른 프레임워크도 그렇지만 지원되는 함수(유저가이드 참고)가 정말 필요한 것들을 집약해놓았습니다.
jquery를 이그나이터의 함수처럼 사용하는 부분도 있고.
폼체크, 페이징, 트랙백, xml, 세션 암호화 등등.. 유저 가이드 대로만 하면 금방 구현. ^^
helper도 마찬가지구요.
모델의 경우 다른 컨트롤을 위해 만든 모델도 로딩시켜서 그냥 쓸 수 있다는거..
common 모델을 만들고 기능별로 따로 만들어서 불러서 쓰는 것이 좋겠죠.
모델에서 데이터 처리후 배열로 뷰파일에 전달, foreach(){ .. }로 처리하기만 하면 되는 뷰.
MVC패턴의 장점이야 두말할 나위가 없구요.
단점으로는 모든 프레임워크가 그렇듯 사용법을 따로 배워야 하죠.
$_POST[‘var’] 로 처리하던 것만 하더라도 $this->input->post(‘var’)로 바꿔서 사용해야 합니다.
$_SERVER 도 마찬가지..
http://www.h.com/index.php/together/mview/index/ 의 주소체계를 사용하다보면 검색후 2페이지로 이동할때 검색어를
http://www.h.com/index.php/together/mview/index/10/검색어 (검색어 부분은 실제로는 urlencode해서 넘깁니다.)의 형태로 넘기게 되는데
간혹 중간에 프로그램 수정에 의해 인자가 추가되는 경우가 있으면 좀 난감해집니다.
그래서 코드이그나이터 포럼에 검색을 해보니 쿠키로 처리하는 경우도 있었고 config.php 파일에서 $config[‘enable_query_strings’] 를 TRUE로 셋팅하여
주소체계를 혼용하여 사용하면 해결이 가능하긴 하지만 그렇게 되면 또 한가지 문제가 생깁니다.
$config[‘enable_query_strings’] = TRUE; –> http://www.h.com/index.php?d=together&c=mview&m=index&page=10&q=검색어 형태의 주소로 사용할 수 있습니다.
이렇게 되면 해결이 되는데 문제는 코드이그나이터의 pagenation 라이브러리 사용에서 문제가 생깁니다.
기존형식으로 사용할때는 잘 작동하던 페이징이 $config[‘enable_query_strings’] = TRUE 가 되면 페이징의 주소가 기존과 다른 형태로 바뀌면서 오작동을 합니다.
그래서 pagenation config 선언할때 한줄을 더 추가해줘야 합니다.
$config[‘page_query_string’] = FALSE; 이 라인이 추가 되어야 문제없이 사용이 됩니다.
설명이 좀 어려운데 실제로 코딩해보시면 이해가 금방 됩니다. ^^;
전 두가지 방법을 다 적용했습니다. 쿠키로 구워서 체크후 일정시간후 날리는 방법과 주소형태를 바꾸는 방법.
그리고 1.7.1 버전에서는 고쳐졌는지 확인을 안해봤는데 제가 사용했던 1.6.3 버전에서는 로그인후 창을 닫으면 세션이 그대로 살아있습니다. 수정하려면 아래 부분 패치
libraries 디렉토리의 Session.php 89 라인
if ($this->sess_expiration == 0)
{
$this->sess_expiration = (60*60*24*365*2);
}
을
if ($this->sess_expiration == 0)
{
$this->sess_expiration = (60*60*24*365*2);
}
else
{
$this->sess_expiration = (60*60*24);
}
로 수정
659라인
setcookie(
$this->sess_cookie_name,
$cookie_data,
– //$this->sess_expiration + time(),
+ ($this->CI->config->item(‘sess_expiration’) == -1) ? 0 : ($this->sess_expiration + time()),
$this->cookie_path,
$this->cookie_domain,
0
);
config.php 파일의 $config[‘permitted_uri_chars’] = ‘a-z 0-9~%.:_=\-‘; 부분도 문제가 됩니다.
주소로 사용할 수 있는 문자를 정규표현식으로 표현한 것이데 간혹 한글을 주소에 사용하기위해 urlencode 했을때 충돌이 납니다.
경우의 수를 다 찾아서 넣어주면 좋겠지만 전 현재 $config[‘permitted_uri_chars’] = ”; 이렇게 사용중입니다.
일단 생각 나는 부분은 여기까지인데 추후에 더 보강하겠습니다. ^^
[펌] 리눅스에서 오라클 rpm 설치 – PHP 연동 추가
출처 http://newgifted.tistory.com/entry/Oracle-10g-Express-%EC%84%A4%EC%B9%98%EB%A6%AC%EB%88%85%EC%8A%A4
오라클을 깔기전에 최소사양을 만족 하는지 확인합니다.
최소 사양은 아래와 같습니다.
RAM 256MB(권장 512MB)
Disk space 1.5GByte
Packages glibc – 2.3.2
libaio – 0.3.96
Swap Space 0~256MB (RAM의 3배 이상)
256~512MB (RAM의 2배 이상)
512MB 이상 (1024GB 이상)
위 사양을 만족 하지 않으면 설치 자체가 불가능 합니다.
만약 설치중 glibc나 libaio패키지 설치를 요구하면 아래와 같이 설치하시면 됩니다.
yum install libaio
또는 직접 다운 받으신후 rpm -Uvh ~~~.rpm을 통해 설치 하셔도됩니다.
우선 오라클 홈페이지에서 Oracle 10g Express 를 받은 후
root계정으로 아래 명령어를 입력하시면 설치가 진행됩니다.
준비 중… ########################################### [100%]
1:oracle-xe-univ ########################################### [100%]
Executing Post-install steps…
You must run ‘/etc/init.d/oracle-xe configure’ as the root user to
configure the database.
설치가 완료된후 데이타 베이스 설정을 해야 됩니다.
아래와 같이 입력하시면 설정을 할 수 있습니다. 설정이 완료된후 언제라도 다시 설정을 바꾸고 싶다면 똑같이 입력 하시면 됩니다.
[root@localhost 신영재]# /etc/init.d/oracle-xe configure
Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Configuration
————————————————-
This will configure on-boot properties of Oracle Database 10g Express
Edition. The following questions will determine whether the database should
be starting upon system boot, the ports it will use, and the passwords that
will be used for database accounts. Press <Enter> to accept the defaults.
Ctrl-C will abort.
Specify the HTTP port that will be used for Oracle Application Express [8080]:HTTP를 통해 편리하게 데이터 베이스를 관리하기 위해 사용할 http포트를 지정합니다. 톰캣 서버와 포트가 같으므로 톰캣 서버를 사용하신다면 다른 포트를 이용하기 위해 다른 포트 번호를 입력 하십시요.
Specify a port that will be used for the database listener [1521]: 다른 서버에어서 DB서버에 접근하기 위한 포트입니다.
Specify a password to be used for database accounts. Note that the same
password will be used for SYS and SYSTEM. Oracle recommends the use of
different passwords for each database account. This can be done after
initial configuration: 암호를 입력 합니다. 이 암호로 SYS, SYSTEM유저로 로그인 가능합니다.
Confirm the password:
Do you want Oracle Database 10g Express Edition to be started on boot (y/n) [y]: 부팅후 자동으로 오라클 DB를 실행할지 여부입니다.
이제 잠시기다리시면.. 설정이 완료됩니다.
Starting Oracle Net Listener…Done
Configuring Database…Done
Starting Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Instance…Done
Installation Completed Successfully.
To access the Database Home Page go to “http://127.0.0.1:8080/apex“
[root@localhost 신영재]#
다음으로 오라클 환경변서 설정이 필요합니다. 다음 디렉토리로 이동합니다.
oracle_env.sh또는 oracle_env.csh스크립트를 실행합니다. 부팅시 계속 해서 자동으로 실행하고 자 하신다면, .bash_profile 또는 .bash_rc에 명령을 넣어 주시면 됩니다.
이제 설치가 완료되었습니다. 아래와 같이 입력하면 DB에 접근 가능합니다. 또는 웹브라우져에서 http://127.0.0.1:8080/apex로 접근하면 아래와 같은 GUI환경을 볼 수 있습니다.
[root@localhost ~]# sqlplus
SQL*Plus: Release 10.2.0.1.0 – Production on 목 1월 25 12:51:05 2007
Copyright (c) 1982, 2005, Oracle. All rights reserved.
사용자명 입력:
위 부분은 리눅스에서 rpm으로 오라클 셋팅, 설치하는 부분입니다.
아래는 php와 연동부분입니다.
예전보다 연동은 무척 간단해졌습니다.
팁 하나
Oracle Database 10g Express Edition Release 10.2.0.1.0 – Production
SQL> EXEC DBMS_XDB.SETLISTENERLOCALACCESS(FALSE); <= 이거 명령어다.
PL/SQL 처리가 정상적으로 완료되었습니다.
SQL>
===================================================================
–> 외부에서 아이피:8080/apex 로 접속이 가능해집니다. 설정후엔 FALSE 대신 TRUE로 바꿔주면 됩니다.
난 centos5.2에 설치했는데 php-devel이 설치 안되어있어서 phpize를 사용할 수 없었다.
그래서 yum install php-devel 후
yum install php-pear 까지 설치한후에
pecl install oci8
그리고 php.ini에 extention=oci8.so 만 추가해주고 아파치 재시작 하면 연동 끝
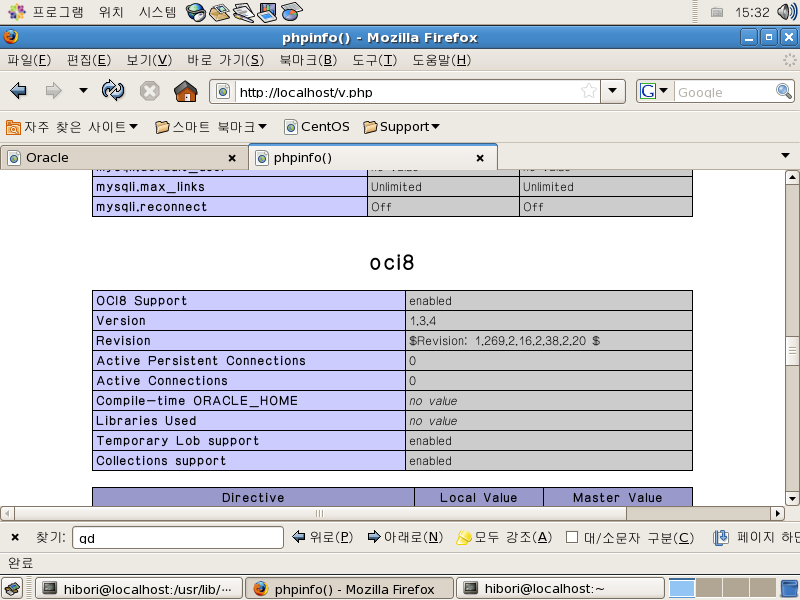
phpinfo(); 함수로 확인해 보니 oci8 이라고 항목이 추가됐다.
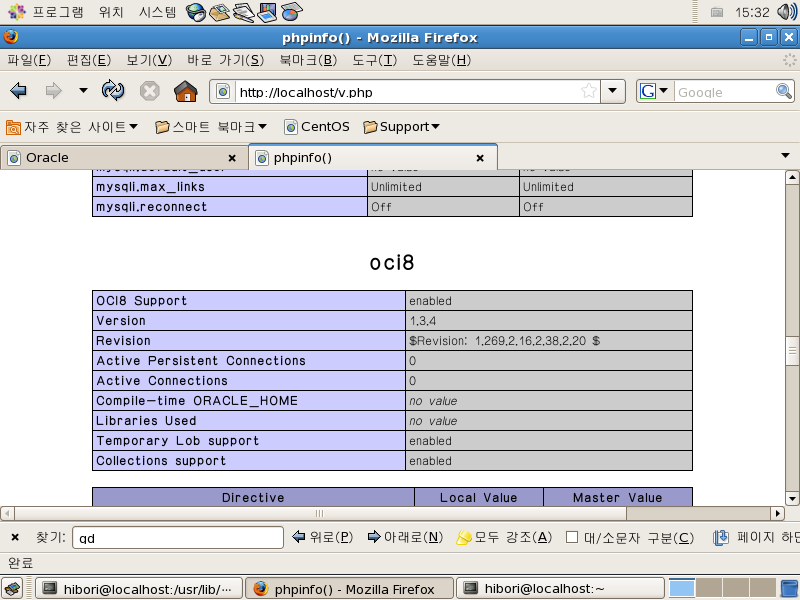
mysql과 oracle 둘다 이상없이 작동.
[펌] PHP 코드를 최적화하는 40가지 팁 (번역)
출처 : http://www.sir.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=pl_php&wr_id=832&page=2 원본은 40 Tips for optimizing your php Code 1. If a method can be static, declare it static. Speed improvement is by a factor of 4. 2. echo is faster than print. 3. Use echo’s multiple parameters instead of string concatenation. 4. Set the maxvalue for your for-loops before and not in the loop. 5. Unset your variables to free memory, especially large arrays. 6. Avoid magic like __get, __set, __autoload 7. require_once() is expensive 8. Use full paths in includes and requires, less time spent on resolving the OS paths. 9. If you need to find out the time when the script started executing, $_SERVER[’REQUEST_TIME’] is preferred to time() 10. See if you can use strncasecmp, strpbrk and stripos instead of regex 11. str_replace is faster than preg_replace, but strtr is faster than str_replace by a factor of 4 12. If the function, such as string replacement function, accepts both arrays and single characters as arguments, and if your argument list is not too long, consider writing a few redundant replacement statements, passing one character at a time, instead of one line of code that accepts arrays as search and replace arguments. 13. It’s better to use select statements than multi if, else if, statements. 14. Error suppression with @ is very slow. 15. Turn on apache’s mod_deflate 16. Close your database connections when you’re done with them 17. $row[’id’] is 7 times faster than $row[id] 18. Error messages are expensive 19. Do not use functions inside of for loop, such as for ($x=0; $x < count($array); $x) The count() function gets called each time. 20. Incrementing a local variable in a method is the fastest. Nearly the same as calling a local variable in a function. 21. Incrementing a global variable is 2 times slow than a local var. 22. Incrementing an object property (eg. $this->prop++) is 3 times slower than a local variable. 23. Incrementing an undefined local variable is 9-10 times slower than a pre-initialized one. 24. Just declaring a global variable without using it in a function also slows things down (by about the same amount as incrementing a local var). PHP probably does a check to see if the global exists. 25. Method invocation appears to be independent of the number of methods defined in the class because I added 10 more methods to the test class (before and after the test method) with no change in performance. 26. Methods in derived classes run faster than ones defined in the base class. 27. A function call with one parameter and an empty function body takes about the same time as doing 7-8 $localvar++ operations. A similar method call is of course about 15 $localvar++ operations. 28. Surrounding your string by ‘ instead of ” will make things interpret a little faster since php looks for variables inside “…” but not inside ‘…’. Of course you can only do this when you don’t need to have variables in the string. 29. When echoing strings it’s faster to separate them by comma instead of dot. Note: This only works with echo, which is a function that can take several strings as arguments. 30. A PHP script will be served at least 2-10 times slower than a static HTML page by Apache. Try to use more static HTML pages and fewer scripts. 31. Your PHP scripts are recompiled every time unless the scripts are cached. Install a PHP caching product to typically increase performance by 25-100% by removing compile times. 32. Cache as much as possible. Use memcached – memcached is a high-performance memory object caching system intended to speed up dynamic web applications by alleviating database load. OP code caches are useful so that your script does not have to be compiled on every request 33. When working with strings and you need to check that the string is either of a certain length you’d understandably would want to use the strlen() function. This function is pretty quick since it’s operation does not perform any calculation but merely return the already known length of a string available in the zval structure (internal C struct used to store variables in PHP). However because strlen() is a function it is still somewhat slow because the function call requires several operations such as lowercase & hashtable lookup followed by the execution of said function. In some instance you can improve the speed of your code by using an isset() trick. Ex. Calling isset() happens to be faster then strlen() because unlike strlen(), isset() is a language construct and not a function meaning that it’s execution does not require function lookups and lowercase. This means you have virtually no overhead on top of the actual code that determines the string’s length. 34. When incrementing or decrementing the value of the variable $i++ happens to be a tad slower then ++$i. This is something PHP specific and does not apply to other languages, so don’t go modifying your C or Java code thinking it’ll suddenly become faster, it won’t. ++$i happens to be faster in PHP because instead of 4 opcodes used for $i++ you only need 3. Post incrementation actually causes in the creation of a temporary var that is then incremented. While pre-incrementation increases the original value directly. This is one of the optimization that opcode optimized like Zend’s PHP optimizer. It is a still a good idea to keep in mind since not all opcode optimizers perform this optimization and there are plenty of ISPs and servers running without an opcode optimizer. 35. Not everything has to be OOP, often it is too much overhead, each method and object call consumes a lot of memory. 36. Do not implement every data structure as a class, arrays are useful, too 37. Don’t split methods too much, think, which code you will really re-use 38. You can always split the code of a method later, when needed 39. Make use of the countless predefined functions 40. If you have very time consuming functions in your code, consider writing them as C extensions 41. Profile your code. A profiler shows you, which parts of your code consumes how many time. The Xdebug debugger already contains a profiler. Profiling shows you the bottlenecks in overview 42. mod_gzip which is available as an Apache module compresses your data on the fly and can reduce the data to transfer up to 80% 43. Excellent Article about optimizing php by John Lim
메쏘드가 static이 될 수 있다면 static으로 선언하라. 4배 빨라진다.
echo가 print보다 빠르다.
문자열을 이어붙이지 말고, echo를 이용하여 여러 개의 파라미터를 적어라.
for 루프을 위핸 최대값(탈출조건)을 루프 안에서가 아니고 루프 시작 이전에 지정하라.
메모리를 해제하기 위해 변수를 unset하라. 특히 커다란 배열은 그래야 된다.
__get, __set, __autoload와 같은 마법을 피해라.
require_once()는 비싸다.
include와 require를 사용할 때, 경로를 찾는데 시간이 적게 걸리는 full path를 사용하라.
스크립트가 언제 실행했는지 알고 싶으면 time()보다 $_SERVER[’REQUEST_TIME’]이 좋다.
정규표현식보다는 가능하면 strncasecmp나 strpbrk, stripos를 사용하라.
* 역주
strncasecmp: 두 문자열의 앞쪽 일부가 대소문자 구분없이 일치하는지 확인할 때 사용
strpbrk: 문자 집합에 속한 특정 문자가 문자열에 나타나는지 확인할 때 사용
stripos: 대소문자 구분없이 특정 문자열이 다른 문자열에 포함되는지 확인할 때 사용
str_replace가 preg_replace보다 빠르지만, strtr은 str_replace보다 4배 빠르다.
만약 문자열 교체 같은 함수가 배열과 문자열을 인자로 받아들이면, 그리고 그 인자 리스트가 길지 않다면, 배열을 한 번에 받아들여서 처리하는 것 대신에 한 번에 문자열을 하나씩 넘겨서 처리하는 것을 고려해봐라.
여러 개의 if/else if 문장 대신에 select 문장을 사용하는 게 더 좋다.
@를 이용한 에러 출력 방지는 매우 느리다.
Apache의 mod_deflate를 켜라.
*역주
mod_deflate는 서버의 출력을 클라이언트에게 보내기 전에 압축하는 모듈임
DB를 다 사용했으면 연결을 닫아라.
$row[’id’]가 $row[id]보다 7배 빠르다.
에러 메시지는 비싸다.
for 루프의 표현식 안에서 함수를 사용하지 마라.
for ($x = 0; $x < count($array); $x)에서 count() 함수가 매번 호출된다.
메쏘드 안에서 지역 변수를 증가시키는 것이 거의 함수 안에서 지역 변수를 호출(증가?)하는 것만큼 빠르다.
전역 변수를 증가시키는 것이 지역 변수를 증가시키는 것보다 2배 느리다.
객체의 멤버변수를 증가시키는 것이 지역 변수를 증가시키는 것보다 3배 느리다.
값이 지정되지 않은 지역 변수를 증가시키는 것이 미리 초기화된 변수를 증가시키는 것보다 9~10배 느리다.
전역 변수를 함수 안에서 사용하지 않으면서 그저 선언하기만 해도 (지역 변수를 증가시키는 것만큼) 느려진다. PHP는 아마 전역 변수가 존재하는지 알기 위해 검사를 하는 것 같다.
메쏘드 호출은 클래스 안에서 정의된 메쏘드의 갯수에 독립적인 듯 하다. 왜냐하면 10개의 메쏘드를 테스트 클래스에 추가해봤으나 성능에 변화가 없었기 때문이다.
파생된 클래스의 메쏘드가 베이스 클래스에서 정의된 것보다 더 빠르게 동작한다.
한 개의 매개변수를 가지고 함수를 호출하고 함수 바디가 비어있다면(함수 내부에서 아무것도 실행하지 않는다면) 그것은 7~8개의 지역변수를 증가시키는 것과 똑같은 시간을 차지한다. 비슷한 메쏘드 호출은 마찬가지로 15개의 지역변수를 증가시키는 연산쯤 된다.
문자열을 이중 따옴표 대신에 단일 따옴표로 둘러싸는 것은 좀 더 빠르게 해석되도록 한다. 왜냐하면 PHP가 이중 따옴표 안의 변수를 찾아보지만 단일 따옴표 안에서는 변수를 찾지 않기 때문이다. 물론 문자열 안에서 변수를 가질 필요가 없을 때만 이렇게 사용할 수 있다.
문자열을 echo할 때 마침표 대신에 쉼표로 분리하는 것이 더 빠르다.
주의: 이것은 여러 문자열을 인자로 받아들이는 함수인 echo로만 작동한다.
Apache에 의해 PHP 스크립트는 정적 HTML 페이지보다 최소 2에서 10배 느리게 서비스된다. 더 많은 정적 HTML 페이지와 더 적은 스크립트를 사용하려고 노력하라.
PHP 스크립트는 캐시되지 않으면 매번 재 컴파일된다. 컴파일 시간을 제거함으로써 25~100%만큼의 성능을 증가시키기 위해 PHP 캐싱 도구를 설치하라.
가능한 한 많이 캐시하라. memcached를 사용하라. memcached는 고성능 메모리 객체 캐싱 시스템이다.
문자열을 가지고 작업하며 문자열이 특정 길이인지 확인할 필요가 있을 때, strlen() 함수를 쓸 것이다. 이 함수는 계산없이 zval 구조체에서 사용할 수 있는 이미 알려진 문자열 길이를 반환하기 때문에 매우 빠르다. 그러나 strlen()이 함수이기 때문에 여전히 조금 느리다. 왜냐하면 함수 호출은 언급된 함수의 실행 뒤에 lowercase와 hashtable lookup같은 여러 개의 연산을 호출하기 때문이다. 어떤 경우에는 isset() 트릭을 이용하여 코드의 스피드를 증가시킬 수도 있다.
if (strlen($foo) < 5) { echo “Foo is too short”; }
vs.
if (!isset($foo{5})) { echo “Foo is too short”; }
isset()을 호출하는 것은 strlen()과는 달리 isset()이 언어 기본문법이고 함수가 아니기 때문에 함수 찾와 lowercase 작업을 필요로 하지 않으므로 strlen()보다 더 빠를 수도 있다. 이것은 가상적으로 문자열의 길이를 결정하는 실제 코드에 과부하가 없다는 것을 의미한다.
변수 $i의 값을 증가시키거나 감소키킬 때, $i++은 ++$i보다 조금 더 느릴 수 있다. 이것은 PHP의 특징이고 다른 언어에는 해당되지 않으니 좀 더 빨라질 것을 기대하면서 C나 Java 코드를 바꾸러 가지 마라. 안 빨라질 것이다. ++$i는 PHP에서 좀 더 빠른데 그것은 $i++에 4개의 opcode가 사용되는 대신에 3개만 필요하기 때문이다. 후증가는 사실 증가될 임시변수의 생성을 초래한다. 반면에 전증가는 원래 값을 직접 증가시킨다. 이것은 opcode가 Zend의 PHP optimizer처럼 최적화하는 최적화 기법의 하나이다. 모든 opcode optimizer들이 이 최적화를 수행하는 것은 아니고 많은 ISP와 server들이 opcode optimizer없이 수행되고 있기 때문에 명심하는 게 좋을 것이다.
모든 것이 OOP일 필요는 없다. 종종 그것은 너무 많은 과부하가 된다. 각각의 메쏘드와 객체 호출은 메모리를 많이 소비한다.
모든 데이터 구조를 클래스로 구현하지 마라. 배열도 유용하다.
메쏘드를 너무 많이 분리하지 마라. 어떤 코드를 정말 재사용할지 생각해봐라.
항상 메쏘드의 코드를 나중에 필요할 때 분리할 수 있다.
수많은 미리 정의된 함수를 활용해라.
매우 시간을 소비하는 함수가 있다면, C 확장으로 작성하는 것을 고려해봐라.
당신의 코드를 프로파일해봐라. 프로파일러는 코드의 어떤 부분이 가장 많은 시간을 소비하는지 보여준다. Xdebug 디버거는 이미 프로파일러를 포함하고 있다. 프로파일링은 전체적인 병목을 보여준다.
Apache 모듈로 사용가능한 mod_gzip은 실행 중에 데이터를 압축하여 전송할 데이터를 80%까지 줄일 수 있다.
John Lim의 PHP를 최적화하는 것에 관한 뛰어난 글
[펌] 간단한 멀티파일 업로더
기본적인틀은 코드프로젝트에서 따왓는데 어딘지 잘 모르겟네요
스크립트 부분만 조금 수정 했습니다.
해당 위치에 uploads폴더를 만들어 줘야 합니다.
코드 프로젝트 소스에서 파일 추가(+ 버튼)을 누르면 그전에 있던 파일명들이 사라지는
현상 때문에 그부분만 고쳐서 올렸습니다.
최대 5개까지 업로드 가능 입니다.
기본적인 옵션들은 수정 하셔서 쓰시면 될듯합니다. ^^
<?php
if($_POST[‘pgaction’]==”upload”)
upload();
else
uploadForm();
//The form having dynamic file uploader
function uploadForm() {
?>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC “-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN” “http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd”>
<html xmlns=”http://www.w3.org/1999/xhtml”>
<head>
<meta http-equiv=”Content-Type” content=”text/html; charset=euc-kr” />
<title> :: FILEUPLOAD :: </title>
</head>
<body bgcolor=”#C8C8C8″ leftmargin=”0″ topmargin=”0″ rightmargin=”0″ bottommargin=”0″>
<br>
<form name=”frm” method=”post” onsubmit=”return validate(this);” enctype=”multipart/form-data”>
<input type=”hidden” name=”pgaction”>
<?php if ($GLOBALS[‘msg’]) { echo ‘<center><span class=”err”>’.$GLOBALS[‘msg’].'</span></center>’; }?>
<input type=’button’ value=’추가’ onclick=’appendItem()’ />
<div id=’itemList’>
<input type=”file” name=”item_file[]”>
</div>
<input type=”submit” value=”Upload File”>
<div id=’debug’ style=”border:1px solid #000″></div>
</form>
<script type=’text/javascript’>
var count =0;
function appendItem()
{
count++;
if(count > 5)
{
alert(“더이상의 파일을 올릴수 없습니다.”);
count = 5;
}
else
{
//log(count);
var newSpanItem = document.createElement(“div”);
newSpanItem.setAttribute(“id”, “item_”+count);
var msg_str = ‘<input type=”file” name=”item_file[]”>’+ ‘<input type=”button” value =”삭제” onclick=”removeItem(‘+count+’)”> ‘;
//var msg_str =”ddd<br>”;
newSpanItem.innerHTML = msg_str;
var itemListNode = document.getElementById(‘itemList’);
itemListNode.appendChild(newSpanItem);
}
}
function removeItem(idCount)
{
var item = document.getElementById(“item_”+ idCount);
if(item != null)
{
item.parentNode.removeChild(item);
}
count –;
}
function validate(f)
{
var chkFlg = false;
for(var i=0; i < f.length; i++)
{
if(f.elements[i].type==”file” && f.elements[i].value != “”)
{
chkFlg = true;
}
}
if(!chkFlg)
{
alert(‘Please browse/choose at least one file’);
return false;
}
f.pgaction.value=’upload’;
return true;
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
<?php
}
//function to store uploaded file
function upload(){
if(count($_FILES[“item_file”][‘name’])>0)
{ //check if any file uploaded
$GLOBALS[‘msg’] = “”; //initiate the global message
for($j=0; $j < count($_FILES[“item_file”][‘name’]); $j++) { //loop the uploaded file array
$filen = $_FILES[“item_file”][‘name’][“$j”]; //file name
$path = ‘uploads/’.$filen; //generate the destination path
if(move_uploaded_file($_FILES[“item_file”][‘tmp_name’][“$j”],$path)) { //upload the file
$GLOBALS[‘msg’] .= “File# “.($j+1).” ($filen) uploaded successfully<br>”; //Success message
}
}
}
else
{
$GLOBALS[‘msg’] = “No files found to upload”; //Failed message
}
uploadForm(); //display the main form
}
?>